Electric Car Components and Functions
Electric Car Components
Electric car or vehicle component and function depend on the car type. There are at least four types of electric cars (Please read the article “Types of Electric Cars, Architecture and Working Principles“) currently sold commercially and operates in the world. This article will discuss various common main electric car components or parts or elements and their function such as traction batteries, inverters (DC-DC converters), traction motors, on-board chargers and controllers. The different types of electric car components determines how the car works. Electric cars (vehicles) components and functions can be explained by means of picture below.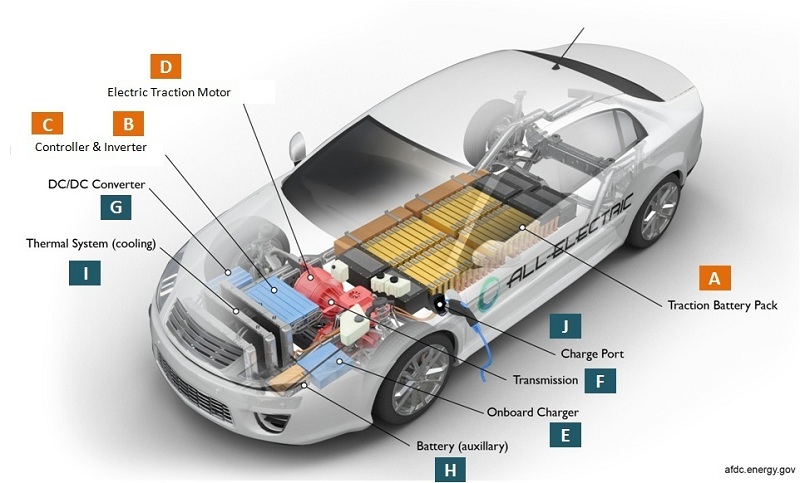
———————————————
How Does An Electric Car Work?
When the car pedal is pressed, then:
- Controller [C] takes and regulates electrical energy from batteries [A] and inverters [B]
- With the controller set, the inverter then sends a certain amount of electrical energy to the motor (according to the depth of pressure on the pedal)
- Electric motor [D] converts electrical energy into mechanical energy (rotation)
- Rotation of the motor rotor rotates the transmission so the wheels turn and then the car moves.
Note: The working principle above is for battery electric vehicle (BEV) type.
———————————————
Electric Vehicle Components
Basic Main Components of Electrical Vehicle
The basic main elements of electric cars installed in almost all types of electric cars are as follows:
Traction Battery Pack (A)
The function of the battery in an electric car is as an electrical energy storage system in the form of direct-current electricity (DC). If it gets a signal from the controller, the battery will flow DC electrical energy to the inverter to then be used to drive the motor. The type of battery used is a rechargeable battery that is arranged in such a way as to form what is called a traction battery pack.
There are various types of electric car batteries. The most widely used is the type of lithium-ion batteries. Please read the article “Electric Car Batteries and Their Characteristics” to get a little idea about batteries for electric cars.
Power Inverter (B)
The inverter functions to change the direct current (DC) on the battery into an alternating current (AC) and then this alternating current is used by an electric motor. In addition, the inverter on an electric car also has a function to change the AC current when regenerative braking to DC current and then used to recharge the battery. The type of inverter used in some electric car models is the bi-directional inverter category.
Controller (C)
The main function of the controller is as a regulator of electrical energy from batteries and inverters that will be distributed to electric motors. While the controller itself gets the main input from the car pedal (which is set by the driver). This pedal setting will determine the frequency variation or voltage variation that will enter the motor, and at the same time determine the car’s speed.
In brief, this unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces. This component will determine how electric car work.
Electric Traction Motor (D)
Because the controller provides electrical power from the traction battery, the electric traction motors will work turning the transmission and wheels. Some hybrid electric cars use a type of generator-motor that performs the functions of propulsion and regeneration. In general, the type of electric motor used is the BLDC (brushless DC) motor
———————————————
Other Electric Car Components
Charger (E) is a battery charging device. Chargers get electricity from outside sources, such as the utility grid or solar power plants. AC electricity is converted into DC electricity and then stored in the battery. There are 2 types of electric car chargers:
- On-board charger: the charger is located and installed in the car
- Off-board charger: the charger is not located or not installed in the car.
Transmission (F): The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
DC/DC Converter (G): This one of electric car parts that to converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Battery (H): In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to power vehicle accessories.
Thermal System – Cooling (I): This system maintains a proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components.
Charge Port (J): The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply in order to charge the traction battery pack.
———————————————







Currently you visiting in our blog please Subscribe for more information.